Hi Maxime and thank you for your quick answer 
Yes, I consider keplerian elements to be my mean elements (they should be the mean elements, aren’t they?).
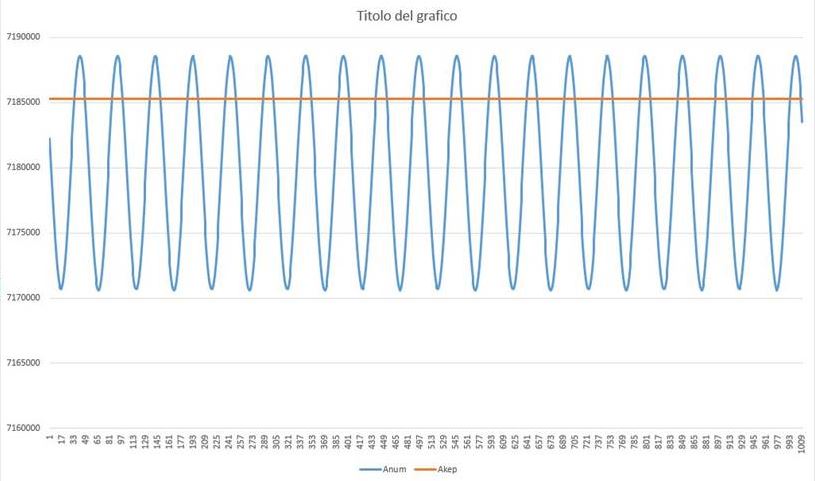
The idea is to use a numerical propagator with a full force model, and than to convert the propagator into a keplerian so that I can obtain the keplerian (constant) orbital parameters.
Hereafter I attached the code that produces the results of the previous figure:
public class PropagatorConversion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Configuration data//
File orekitData = new File("orekit-data");
DataProvidersManager manager = DataProvidersManager.getInstance();
manager.addProvider(new DirectoryCrawler(orekitData));
//////////////////////
// gravity field
NormalizedSphericalHarmonicsProvider provider = GravityFieldFactory.getNormalizedProvider(2, 0);
double mu = provider.getMu();
// inertial frame
Frame inertialFrame = FramesFactory.getEME2000();
// Initial date
AbsoluteDate initialDate = new AbsoluteDate(2022,11,01,1,48,9.303,
TimeScalesFactory.getUTC());
// Initial orbit
final double a = 7182.25536152*1000; // semi major axis in meters
final double e = 0.00111776; // eccentricity
final double i = FastMath.toRadians(98.73774250); // inclination
final double omega = FastMath.toRadians(65.11464822); // perigee argument
final double raan = FastMath.toRadians(2.23553023); // right ascention of ascending node
final double TA = FastMath.toRadians(151.17294416); // true anomaly
Orbit initialOrbit = new KeplerianOrbit(a, e, i, omega, raan, TA, PositionAngle.TRUE,
inertialFrame, initialDate, mu);
final double period = initialOrbit.getKeplerianPeriod();
// Initial state definition
final SpacecraftState initialState = new SpacecraftState(initialOrbit);
// Adaptive step integrator with a minimum step of 0.001 and a maximum step of 1000
final double minStep = 0.001;
final double maxStep = 1000.;
final double dP = 1.e-2;
final OrbitType orbType = OrbitType.CARTESIAN;
final double[][] tol = NumericalPropagator.tolerances(dP, initialOrbit, orbType);
final AbstractIntegrator integrator = new DormandPrince853Integrator(minStep, maxStep,
tol[0], tol[1]);
// Propagator
NumericalPropagator numProp = new NumericalPropagator(integrator);
numProp.setInitialState(initialState);
numProp.setOrbitType(orbType);
//Propagator Force Model////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //
//1) Gravity Field & Third Body //
//
ForceModel holmesFeatherstone = //
new HolmesFeatherstoneAttractionModel(FramesFactory.getITRF(IERSConventions.IERS_2010,true),provider); //
numProp.addForceModel(holmesFeatherstone); //
numProp.addForceModel(new ThirdBodyAttraction(CelestialBodyFactory.getSun())); //
numProp.addForceModel(new ThirdBodyAttraction(CelestialBodyFactory.getMoon())); //
//
//2) Drag //
final DragForce drag = //
new DragForce(new HarrisPriester(CelestialBodyFactory.getSun(), //
new OneAxisEllipsoid(Constants.WGS84_EARTH_EQUATORIAL_RADIUS, //
Constants.WGS84_EARTH_FLATTENING, //
FramesFactory.getITRF(IERSConventions.IERS_2010, true))), //
new IsotropicDrag(2.5, 1.2)); //
numProp.addForceModel(drag); //
//
//3) Solar Radiation Pressure //
ExtendedPVCoordinatesProvider sun = CelestialBodyFactory.getSun(); //
OneAxisEllipsoid earth = //
new OneAxisEllipsoid(6378136.46, 1.0 / 298.25765, //
FramesFactory.getITRF(IERSConventions.IERS_2010, true)); // //
SolarRadiationPressure SRP = //
new SolarRadiationPressure(sun, earth.getEquatorialRadius(), //
(RadiationSensitive) new IsotropicRadiationSingleCoefficient(1.2, 1.2)); //
numProp.addForceModel(SRP); //
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Propagator factory
PropagatorBuilder builder = new KeplerianPropagatorBuilder(initialOrbit, PositionAngle.TRUE, dP);
// Propagator converter
PropagatorConverter fitter = new FiniteDifferencePropagatorConverter(builder, 1.e-6, 5000);
// Resulting propagator
KeplerianPropagator kepProp = (KeplerianPropagator)fitter.convert(numProp, 2*period, 251);
// Step handlers
StatesHandler numStepHandler = new StatesHandler();
StatesHandler kepStepHandler = new StatesHandler();
// Set up operating mode for the propagator as master mode
// with fixed step and specialized step handler
numProp.setMasterMode(60., numStepHandler);
kepProp.setMasterMode(60., kepStepHandler);
// Extrapolate from the initial to the final date
numProp.propagate(initialDate, initialDate.shiftedBy(10.*period));
kepProp.propagate(initialDate, initialDate.shiftedBy(10.*period));
// retrieve the states
List<SpacecraftState> numStates = numStepHandler.getStates();
List<SpacecraftState> kepStates = kepStepHandler.getStates();
// Print the results on the output file
System.out.println("Mean SMA (constant):"+ kepProp.getInitialState().getA());
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("Osculating SMA");
for (SpacecraftState numState : numStates) {
for (SpacecraftState kepState : kepStates) {
if (numState.getDate().compareTo(kepState.getDate()) == 0) {
System.out.println(numState.getA());
break;
}
}
}
}
/** Specialized step handler.
* <p>This class extends the step handler in order to handle states at each step.<p>
*/
private static class StatesHandler implements OrekitFixedStepHandler {
/** Points. */
private final List<SpacecraftState> states;
public StatesHandler() {
// prepare an empty list of SpacecraftState
states = new ArrayList<SpacecraftState>();
}
public void handleStep(SpacecraftState currentState, boolean isLast) {
// add the current state
states.add(currentState);
}
/** Get the list of handled orbital elements.
* @return orbital elements list
*/
public List<SpacecraftState> getStates() {
return states;
}
}
}
I will see also the DSST propagator, as you suggested.
Thank you!!
Giacomo
![]()