Hi,
I am currently working on verifying the accuracy of my Orekit propagator. My goal is to achieve an accuracy of less than 100 meters over a period of 5 days or more. Ideally, I need the highest accuracy possible. To assess my propagator’s performance, I am comparing its results against STK HPOP. I also compared the STK HPOP results with GMAT for verification, and they were nearly identical.
While I am aware that more precise data is available in SP3 products from CDDIS, I am unsure how to extract the positional (x, y, z) and velocity (vx, vy, vz) data from these files for a LEO satellite over a specific time window.
For the comparison, I am using the same configuration in both HPOP and Orekit, with data from the Hubble Space Telescope (referenced in this paper: Hubble Fact Sheet). I chose Hubble due to its LEO orbit, as I am interested in comparing results for satellites at this altitude.
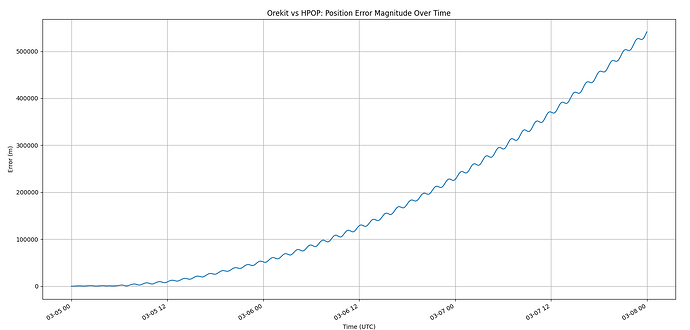
The comparison is done using the same drag coefficient, solar radiation pressure, identical starting timestamps, same reference frame (EME2000 for Orekit and J2000 for STK), time step of 10 seconds… However, when comparing my Orekit propagator, the error is significantly higher, as shown in the plot. I have double-checked my code to ensure that the comparisons and plotting are correct.
I have considered using SP3 products from CDDIS for a more accurate comparison, but I am uncertain about how to extract the required data for a LEO satellite for the given time period. If I can manage this, the comparison between my Orekit propagator and the SP3 data would provide much more precise results.
I have attached the code for my propagator and the comparison results for your reference.
There is obviously something wrong ![]()
import orekit
from orekit.pyhelpers import setup_orekit_curdir, download_orekit_data_curdir
import os
import logging
from java.io import File
from org.orekit.utils import IERSConventions, Constants
from org.orekit.propagation.numerical import NumericalPropagator
from org.orekit.forces.gravity import HolmesFeatherstoneAttractionModel
from org.orekit.forces.gravity.potential import GravityFieldFactory
from org.orekit.forces.drag import DragForce, IsotropicDrag
from org.orekit.forces.radiation import (
SolarRadiationPressure,
IsotropicRadiationSingleCoefficient,
)
from org.orekit.models.earth.atmosphere import NRLMSISE00
from org.orekit.models.earth.atmosphere.data import CssiSpaceWeatherData
from org.orekit.bodies import CelestialBodyFactory, OneAxisEllipsoid
from org.orekit.frames import FramesFactory
from org.orekit.orbits import CartesianOrbit, OrbitType, KeplerianOrbit
from org.orekit.time import AbsoluteDate, TimeScalesFactory
from org.orekit.utils import PVCoordinates
from org.hipparchus.ode.nonstiff import DormandPrince853Integrator
from org.hipparchus.geometry.euclidean.threed import Vector3D
from org.orekit.propagation import SpacecraftState
from org.orekit.forces.gravity import ThirdBodyAttraction
from org.orekit.forces.gravity import Relativity
from org.orekit.forces.gravity import OceanTides, SolidTides
import math
import numpy as np
# Initialize Orekit
orekit.initVM()
setup_orekit_curdir()
# Download Orekit data if not already available
if not os.path.isdir("orekit-data"):
download_orekit_data_curdir()
# Configure logging
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO,
format="%(asctime)s [%(levelname)s] %(message)s",
)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# 0. Set up constants
initial_state = [
-4202.835033e3,
-5275.624112e3,
-1327.976733e3,
5.740649e3,
-3.738504e3,
-3.330234e3,
] # m/s
mass = 11063.1 # kg
drag_coeff = 2.47
drag_area = 66.975 # m²
srp_coeff = 1.5
srp_area = 266.975 # m²
start_date = AbsoluteDate(2025, 3, 4, 23, 58, 50.815, TimeScalesFactory.getUTC())
# end_date = start_date.shiftedBy(100.0) # for testing purposes
end_date = AbsoluteDate(
2025, 3, 9, 23, 58, 50.815, TimeScalesFactory.getUTC()
) #propagation for 5 days
step_size = 10.0 # seconds
file_path = "orekit_data.txt"
# 1. Set up Earth parameters
earth = CelestialBodyFactory.getEarth()
earthFrame = FramesFactory.getEME2000()
earthRadius = Constants.WGS84_EARTH_EQUATORIAL_RADIUS
earthFlattening = Constants.WGS84_EARTH_FLATTENING
earthShape = OneAxisEllipsoid(earthRadius, earthFlattening, earthFrame)
# 2. Set up Earth gravity model
gravity_provider = GravityFieldFactory.getNormalizedProvider(100, 100)
eme2000Frame = FramesFactory.getEME2000()
gravity_model = HolmesFeatherstoneAttractionModel(eme2000Frame, gravity_provider)
# 3. Create initial orbit - Use EME2000 frame instead of ITRF
pvCoordinates = PVCoordinates(
Vector3D(initial_state[0], initial_state[1], initial_state[2]),
Vector3D(initial_state[3], initial_state[4], initial_state[5]),
)
# Change to EME2000 frame
initial_orbit = CartesianOrbit(
pvCoordinates, FramesFactory.getEME2000(), start_date, Constants.WGS84_EARTH_MU
)
# 4. Set up numerical propagator
min_step = 1e-3
max_step = 500.0
init_step = 60.0
# For extracting tolerances if is needed, for now I hard-code 1e-13 when
# construting the integrator instance
# position_tolerance = 1e-4
# velocity_tolerance = 1e-5
integrator = DormandPrince853Integrator(min_step, max_step, 1e-13, 1e-13)
integrator.setInitialStepSize(init_step)
propagator = NumericalPropagator(integrator)
propagator.setOrbitType(OrbitType.CARTESIAN)
propagator.setInitialState(SpacecraftState(initial_orbit, mass))
propagator.setMu(Constants.WGS84_EARTH_MU)
# 5. Add force models
# 5.1. Add gravity model
propagator.addForceModel(gravity_model)
# 5.2. Add atmospheric drag model
cssiSpaceWeatherData = CssiSpaceWeatherData("SpaceWeather-All-v1.2.txt")
atmosphere = NRLMSISE00(cssiSpaceWeatherData, CelestialBodyFactory.getSun(), earthShape)
dragSC = IsotropicDrag(drag_area, drag_coeff)
drag_force = DragForce(atmosphere, dragSC)
propagator.addForceModel(drag_force)
# 5.3. Add solar radiation pressure model
sun = CelestialBodyFactory.getSun()
isotropicRadiationSingleCoeff = IsotropicRadiationSingleCoefficient(srp_area, srp_coeff)
srpForce = SolarRadiationPressure(sun, earthShape, isotropicRadiationSingleCoeff)
propagator.addForceModel(srpForce)
# 5.4 Add third body forces models
propagator.addForceModel(ThirdBodyAttraction(CelestialBodyFactory.getSun()))
propagator.addForceModel(ThirdBodyAttraction(CelestialBodyFactory.getMoon()))
# For further precision (m/cm resolution)
# # 5.5 Add relativity effects
# propagator.addForceModel(Relativity(Constants.EIGEN5C_EARTH_MU))
# # 5.6 Add ocean tides
# propagator.addForceModel(
# OceanTides(FramesFactory.getEME2000())
# )
# propagator.addForceModel(
# SolidTides(FramesFactory.getEME2000())
# )
# 6. Propagation and data output
logger.info(f"Starting propagation at {start_date}")
try:
with open(file_path, "w") as file:
logger.info(
f"Initial altitude: {pvCoordinates.getPosition().getNorm() - earthRadius} m"
)
# Propagation in time steps of 10 seconds
sample_date = start_date
while sample_date.compareTo(end_date) <= 0:
state = propagator.propagate(sample_date)
# Get coordinates in EME2000 frame
pv = state.getPVCoordinates(FramesFactory.getEME2000())
pos = pv.getPosition()
vel = pv.getVelocity()
altitude = pos.getNorm() - earthRadius
logger.info(f"Date: {state.getDate()}, Pos: {pos} m, Vel: {vel} m/s")
# Save in file
utc_date = (
state.getDate().toString(TimeScalesFactory.getUTC()).replace("T", " ")
)
line = f"{utc_date},{pos.getX()},{pos.getY()},{pos.getZ()},{vel.getX()},{vel.getY()},{vel.getZ()}\n"
file.write(line)
# Advance 10 seconds
sample_date = sample_date.shiftedBy(10.0)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"An error occurred: {e}")
finally:
logger.info(f"Propagation finished at {end_date}")
logger.info(f"Propagation data saved to {file_path}")